1. **Q: Can alopecia be cured?**
– **A:** The outcome depends on the type and cause of alopecia. Some types, such as androgenetic alopecia, may not have a cure but can be managed with treatments to slow down hair loss and promote growth. Other types, like alopecia areata, may resolve on their own or respond well to treatment.
2. **Q: Is there an effective over-the-counter treatment for baldness?**
– **A:** Minoxidil is an over-the-counter topical medication that has been FDA-approved for both men and women with androgenetic alopecia. It is commonly used to stimulate hair growth and slow down hair loss.
3. **Q: How does finasteride work, and is it suitable for women?**
– **A:** Finasteride inhibits the action of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and is primarily used for male pattern baldness. It is not recommended for use in women of childbearing age due to potential risks during pregnancy.
4. **Q: Are there natural remedies for alopecia?**
– **A:** Some people explore natural remedies such as essential oils, aloe vera, or dietary supplements like biotin. While these may have anecdotal support, scientific evidence is often limited, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before relying solely on natural remedies.
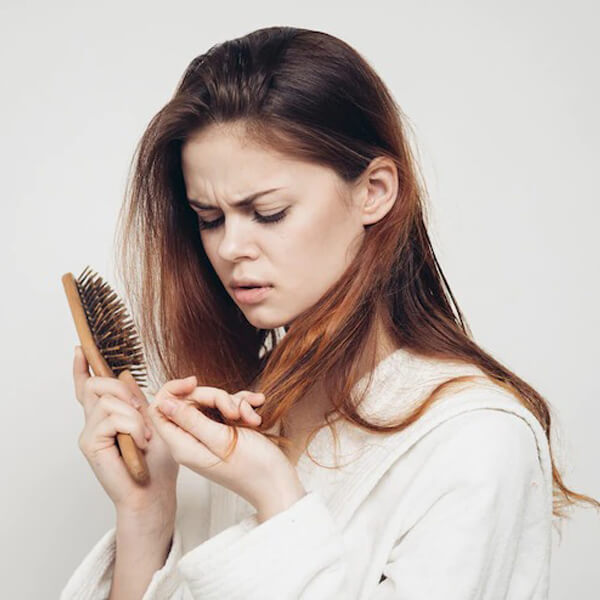
5. **Q: Can stress cause hair loss, and how can it be managed?**
– **A:** Stress can contribute to hair loss, and managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, and relaxation exercises may help. Identifying and addressing underlying stressors is crucial.
6. **Q: Are there side effects of using minoxidil or finasteride?**
– **A:** Both minoxidil and finasteride can have side effects. Common side effects of minoxidil may include scalp irritation, while finasteride can potentially cause sexual side effects in men. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare professional.
7. **Q: How long does it take to see results from hair loss treatments?**
– **A:** The timeline for results varies among individuals and depends on the specific treatment. Minoxidil users, for example, may start to see results in a few months. Patience is often required.
8. **Q: Can alopecia areata be treated with corticosteroids alone?**
– **A:** Corticosteroids are a common treatment for alopecia areata. They can be applied topically, injected into the affected areas, or taken orally. In some cases, other treatments or a combination of therapies may be recommended.
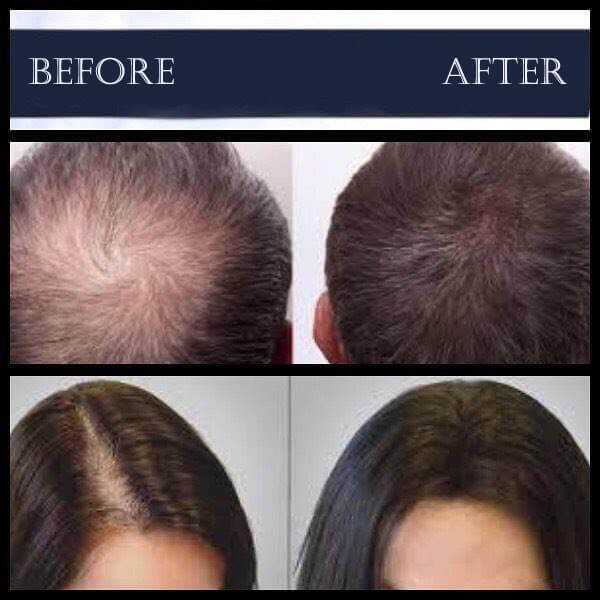
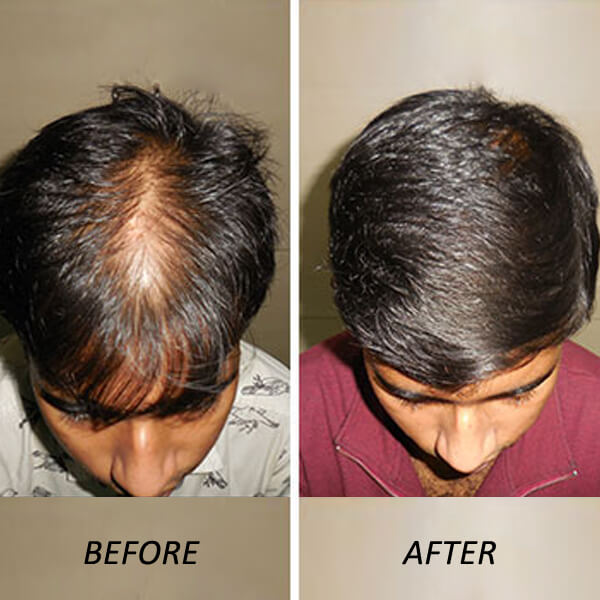
9. **Q: Is hair transplantation a permanent solution for baldness?**
– **A:** Hair transplantation involves moving hair follicles from one area of the body to another. While it can provide a long-lasting solution, the success of the procedure depends on factors like the quality of donor hair and the skill of the surgeon.
10. **Q: Can lifestyle changes improve hair health?**
– **A:** Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute to overall well-being, which may indirectly support hair health.
Always consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for personalized advice based on your specific condition and needs.